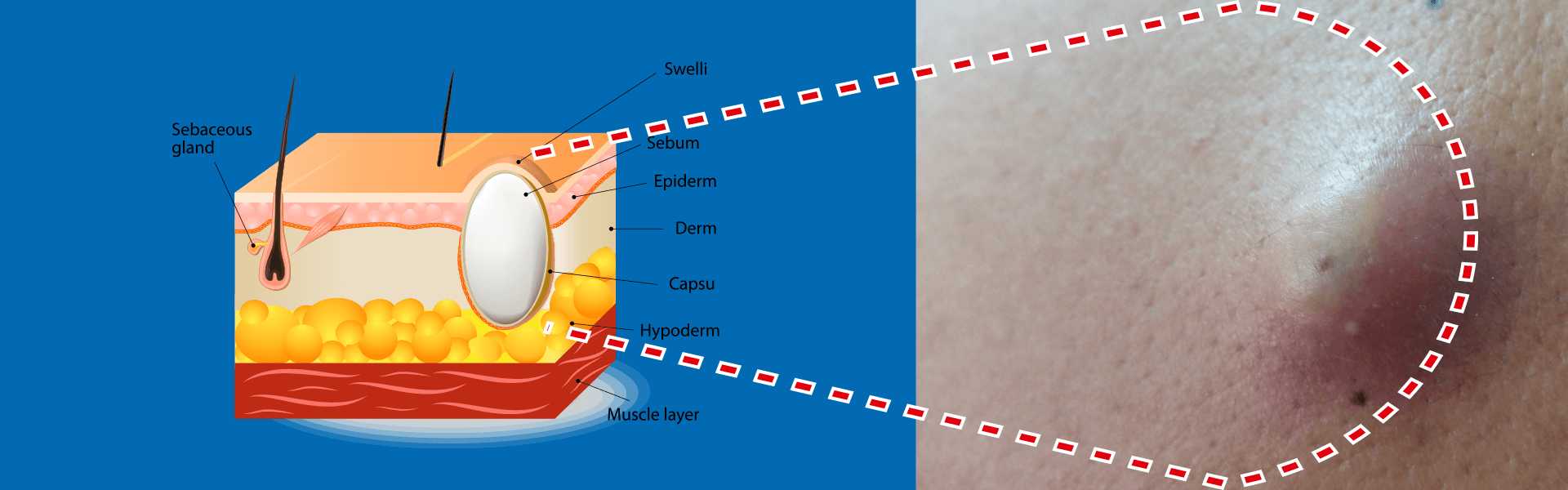
Sebaceous Cyst Diagnosis
Diagnosing a sebaceous cyst typically involves a comprehensive examination by a medical professional such as a dermatologist or plastic/cosmetic surgeon. The diagnostic process includes:
Medical History: The initial step involves obtaining the patient's medical history, including information about symptoms, cyst duration, and any pertinent past medical conditions or surgeries.
Physical & Visual Exam: The doctor performs a physical examination to assess the affected area, observing the cyst's size, appearance, location, and associated symptoms. Additionally, the cyst's characteristics, including the central punctum, shape, and firmness, are evaluated.
These examinations help the doctor differentiate the fluid-filled lump from other conditions such as lipomas, epidermoid cysts, and other types of skin lesions. To aid in differentiation, certain tests may be recommended:
Ultrasound: Utilizing sound waves, an ultrasound scan generates images of the cyst and surrounding tissues. This aids in determining the cyst's size, location, and internal structure, helping to distinguish cysts from other types of masses.
Biopsy: If there is suspicion of cancer in the cyst, a biopsy is conducted. During this procedure, a tissue sample is taken and sent to a laboratory for examination, confirming the diagnosis.
Other Imaging Tests: In rare instances, particularly if the cyst is deep-seated or if there are concerns about potential connections with underlying structures, an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computed tomography) scan may be performed. These tests provide detailed images of internal structures and surrounding tissues.
Sebaceous Cyst Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available for sebaceous cysts, with the choice depending on factors such as the cyst's severity, symptoms, and patient preference. Common treatment options include:
Observation: For small, asymptomatic cysts without complications, monitoring without active treatment may be recommended. Regular observation allows individuals to track cyst growth. If it continues to enlarge, medical intervention to remove the cyst becomes necessary.
Drainage: In cases of infection or inflammation, the doctor may perform a drainage procedure, which involves making a small incision in the cyst to release accumulated fluid or pus. After drainage, sterile gauze is applied to promote healing.
Surgical Excision: Surgical excision is the most effective treatment for sebaceous cysts. It involves complete removal of the cyst and its surrounding capsule, known as the cyst wall. Surgical excision is often advised for large cysts, symptomatic or painful cysts, or those at risk of infection or recurrence.
Laser Treatment: Laser treatment may be utilized in specific situations, involving the use of a laser to vaporize the cyst and its wall, completely eliminating it. This method is less invasive and may result in minimal scarring compared to traditional surgical excision.
While medically recommended treatments are available, there are also home remedies, ayurvedic medicine, homeopathic remedies, etc., marketed for sebaceous cyst removal. However, the effectiveness of these methods is unverified.