Sinus Types:
Ethmoid Sinus: Situated between the eyes
Frontal Sinus: Located behind the forehead
Maxillary Sinus: Positioned behind the cheekbones
Sphenoid Sinus: Situated beneath the base of the skull
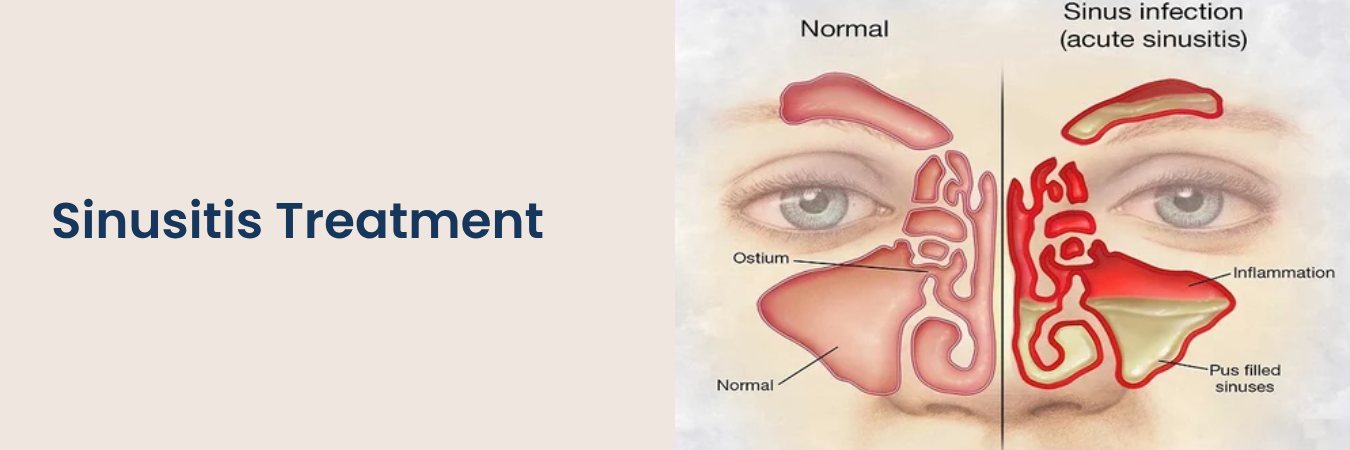
Sinusitis Variations (Sinus Infection):
Acute Sinusitis: Lasting 2 to 4 weeks
Subacute Sinusitis: Persisting 4 to 12 weeks
Chronic Sinusitis: Extending for 12 weeks or more
Recurrent Sinusitis: Occurring multiple times within a year
Common Symptoms of Sinusitis:
- Intense headache
- Facial pressure or discomfort
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Breathing difficulties
- Diminished sense of smell
- Swelling around eyes, nose, or cheeks
- Nasal inflammation
Diagnostic Tests and Treatment:
Diagnostic Tests:
To comprehend your sinus infection, your surgeon will recommend various pre-operative tests, including:
Imaging Tests: Such as CT Scans and X-rays, to identify the root cause of swelling, inflammation, and blockage.
Allergy Test: To ascertain if allergies contribute to nasal blockage.
Nasal Endoscopy: Employing a thin, flexible endoscopic fiber tool to identify potential culprits like nasal polyps, deviated nasal septum, tumors, etc.
Swab Test: Analyzing nasal discharge samples to distinguish bacterial or viral infection.
Sinusitis Treatment - Medication or Self-Care:
Initial sinusitis treatment often involves a combination of medication and self-care:
Antibiotics: Effective for bacterial infections, not viral ones.
Nasal Sprays: Decongestant sprays open blocked sinuses, but overuse can worsen congestion.
Humidifier: Maintains air moisture, alleviating dryness and congestion.
Steam Inhalation: Relieves nasal swelling, pain, and congestion.
Hydration: Drinking fluids thins mucus and eases congestion.
Sinusitis Treatment - Surgical Approach:
For chronic cases unresponsive to medications, surgery becomes an option:
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS): A minimally invasive procedure lasting 1 to 3 hours.
Surgical Steps:
Anesthesia: Nasal area is sedated.
Endoscopy: Infected bone, tissue, or polyps are removed.
Burr Usage: In some cases, a rotating burr scrapes tissue.
Nasal Packing: Absorbs blood or discharge.
For comprehensive sinusitis treatment, Pilot Heal offers FESS performed by skilled ENT specialists. Reach out to us for an appointment and expert care.