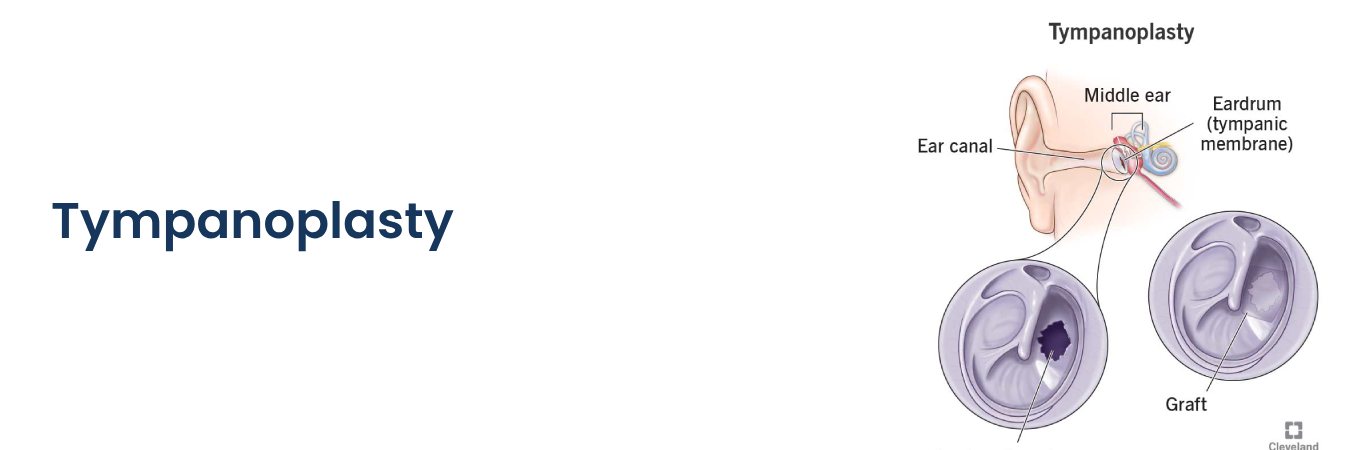Advantages of Tympanoplasty:
- Enhanced hearing capabilities
- Reduction in recurrent ear discharge
- Diminished likelihood of ear infections
- Minimized potential for earaches
- Rectification of tympanic membrane perforation
Why Opt for Advanced Tympanoplasty?
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Accelerated recovery period
- Decreased risk possibilities
- Minimal blood loss
Tympanoplasty Treatment: Diagnosis and Procedure
Diagnosing Hearing Impairment:
Before embarking on hearing loss treatment, an accurate diagnosis is essential to identify the root cause and extent of the ear condition. Common diagnostic tests used to identify hearing issues include:
Physical Examination: The doctor examines the ear canal using light to identify potential factors like earwax buildup, inflammation due to infections, structural abnormalities, etc. A whisper test may also be conducted, covering one ear to assess hearing at varying sound levels.
Tuning Fork Tests: These tests employ a tuning fork to detect hearing loss and pinpoint the affected area within the ear.
Audiometer Tests: Audiometer tests ascertain the softest audible sound.
Surgical Interventions for Hearing Loss:
Four primary types of ear surgeries are utilized to rectify hearing loss:
Myringoplasty: This procedure involves patching a hole in the eardrum by replacing the tympanic membrane with a graft from another part of the body.
Ossiculoplasty: Ossiculoplasty reconstructs the middle ear ossicular chain to restore sound/vibration transmission through the middle ear.
Tympanoplasty: Tympanoplasty repairs a ruptured eardrum to alleviate hearing loss or prevent recurring ear infections.
Mastoidectomy: A mastoidectomy reshapes or restructures the mastoid bone to address diseased cells or hearing loss.
After diagnosis, your surgeon will guide you through pre-surgery preparations. Ear surgery may be performed endoscopically or through open methods. Typically, a small, inconspicuous scar may result after endoscopic surgery. Corrections are made by the surgeon, followed by the closure of the incision with small sutures.